There are two ways to connect with the Guest Operating System:-
1. vSphere Web Client > vCenter Server > Select ESXi Host > Select VM > Open Console.
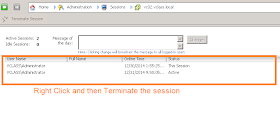
and then you can check the sessions and terminate the session when you will terminate the session from here then it will terminate the VM console as well.
 2. RDP Client > Connect with VM through IP or Name.
2. RDP Client > Connect with VM through IP or Name.
Run the command quser or tsadmin to view the session and then from the tsadmin console you can terminate the particular session
Generally Second Option is used by the system admins and first option is used by the vmware admin to access the guest os.
1. vSphere Web Client > vCenter Server > Select ESXi Host > Select VM > Open Console.
and then you can check the sessions and terminate the session when you will terminate the session from here then it will terminate the VM console as well.
 2. RDP Client > Connect with VM through IP or Name.
2. RDP Client > Connect with VM through IP or Name.Run the command quser or tsadmin to view the session and then from the tsadmin console you can terminate the particular session
Generally Second Option is used by the system admins and first option is used by the vmware admin to access the guest os.


